
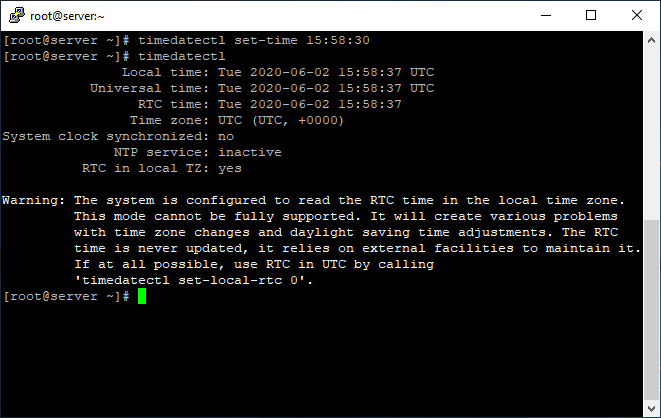
Most top-level domains are managed by ICANN/IANA. there are currently over 1500 top-level domains. There is a DNS zone for each Top Level Domain, such as “.com”, “.org” or country codes like “.co.uk”. Any recursive DNS query (learn more about DNS query types) starts by contacting one of these root servers, and requesting details for the next level down the tree-the Top Level Domain (TLD) server. The DNS root zone is operated by 13 logical servers, run by organizations like Verisign, the U.S. Since 2016, the root zone is overseen by the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN), which delegates management to a subsidiary acting as the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). The root of the DNS system, represented by a dot at the end of the domain name-for example. Acme assumes responsibility for setting up an authoritative DNS server that holds the correct DNS records for the domain.Īt each hierarchical level of the DNS system, there is a Name Server containing a zone file, which holds the trusted, correct DNS records for that zone. Each of these levels can be a DNS zone.įor example, the root domain “” may be delegated to a Acme Corporation. The Domain Name System (DNS) defines a domain namespace, which specifies Top Level Domains (such as “.com”), second-level domains, (such as “”) and lower-level domains, also called subdomains (such as “”). The authoritative name server then resolves the DNS lookup by providing the IP address, or other data, for the requested hostname. This server is called the authoritative name server for the domain. When a web browser or other network device needs to find the IP address for a hostname such as “”, it performs a DNS lookup - essentially a DNS zone check - and is taken to the DNS server that manages the DNS zone for that hostname. A DNS zone is also an administrative function, allowing for granular control of DNS components, such as authoritative name servers. Stay tuned for future updates.A DNS zone is a distinct part of the domain namespace which is delegated to a legal entity-a person, organization or company, who are responsible for maintaining the DNS zone. For any queries, do not hesitate to ask them in the comments section. Successful execution of this file will also change the timezone to the required one. sudo cp /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Calcutta /etc/localtime

cp /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Calcutta /etc/localtimeįor non ROOT users, run command with sudo privileges. Successful execution of above command will change the timezone to IST.Ģ. We can copy the data of required zone file to “/etc/localtime” file. sudo ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Calcutta /etc/localtime ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Calcutta /etc/localtimeįor non ROOT users, run command with sudo privileges. We can create a soft link to file “/etc/localtime” and link it to the required zone file. To change the time zone in Linux we can use any of one method listed below. Basically, we are going to change our machine time to IST. In this tutorial, we are going the change the timezone of our machine to Calcutta city located in India, Continent is Asia.
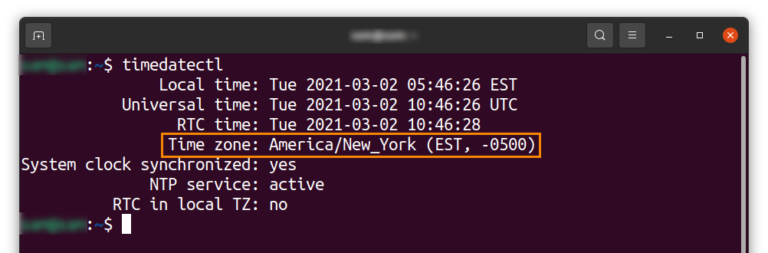
These directories further contain the zone files for different cities. You will also find some directories inside this location. Listing the directory at that location will provide us with a list of various time zones available in Linux. Linux system fetches the local time and timezone information from file “/etc/localtime” Directory Containing the Time Zone in Linuxĭirectory “/usr/share/zoneinfo” contains the list of time zone data files. Instructions for changing the time zone on Amazon ec2 instances. Instruction for changing the time zone on Ubuntu. Instructions for changing the time zone on Centos. This tutorial contains the detailed instructions for changing the timezone on various distributions of Linux. In our day to day life, we come across certain circumstances where the need of changing and setting up the different timezone on Linux system originates consistently. Selection of the standard and precise timezone is crucial for evaluation and execution of many tasks and processes running on a Linux instance.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
